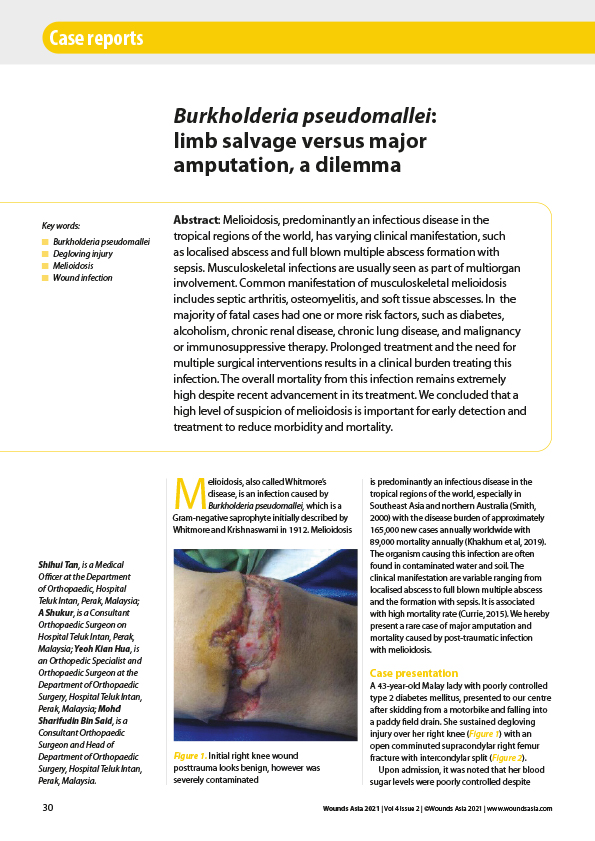
Melioidosis, predominantly an infectious disease in the
tropical regions of the world, has varying clinical manifestation, such
as localised abscess and full blown multiple abscess formation with
sepsis. Musculoskeletal infections are usually seen as part of multiorgan
involvement. Common manifestation of musculoskeletal melioidosis
includes septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, and soft tissue abscesses. In the
majority of fatal cases had one or more risk factors, such as diabetes,
alcoholism, chronic renal disease, chronic lung disease, and malignancy
or immunosuppressive therapy. Prolonged treatment and the need for
multiple surgical interventions results in a clinical burden treating this
infection. The overall mortality from this infection remains extremely
high despite recent advancement in its treatment. We concluded that a
high level of suspicion of melioidosis is important for early detection and
treatment to reduce morbidity and mortality.