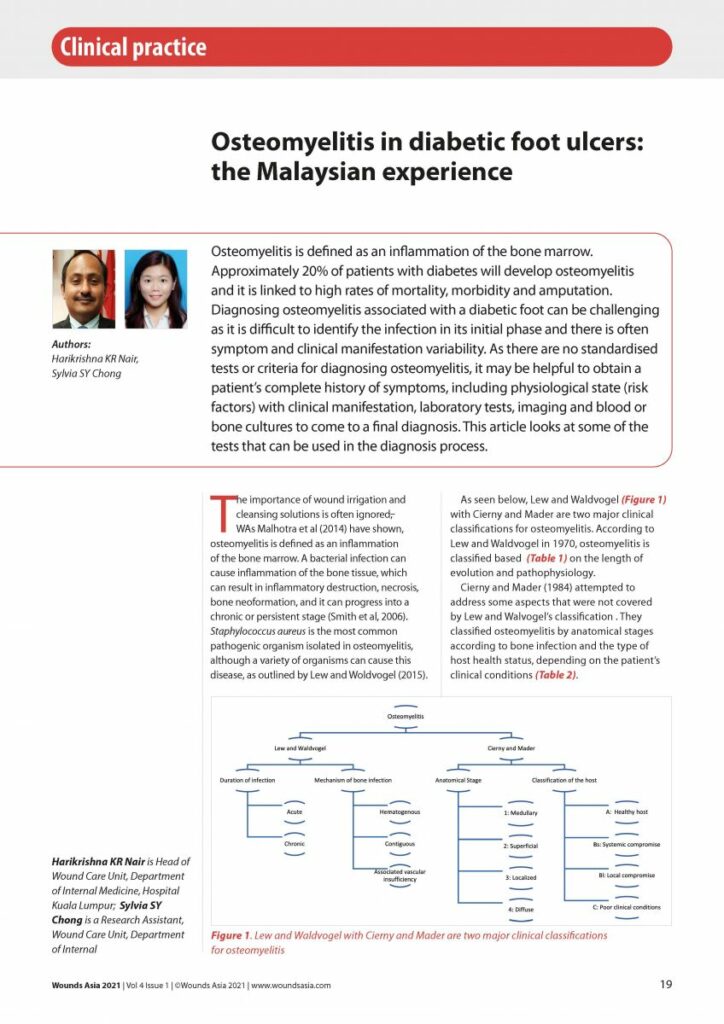
Osteomyelitis is defined as an inflammation of the bone marrow. Approximately 20% of patients with diabetes will develop osteomyelitis and it is linked to high rates of mortality, morbidity and amputation. Diagnosing osteomyelitis associated with a diabetic foot can be challenging as it is difficult to identify the infection in its initial phase and there is often symptom and clinical manifestation variability. As there are no standardised tests or criteria for diagnosing osteomyelitis, it may be helpful to obtain a patient’s complete history of symptoms, including physiological state (risk factors) with clinical manifestation, laboratory tests, imaging and blood or bone cultures to come to a final diagnosis. This article looks at some of the tests that can be used in the diagnosis process.