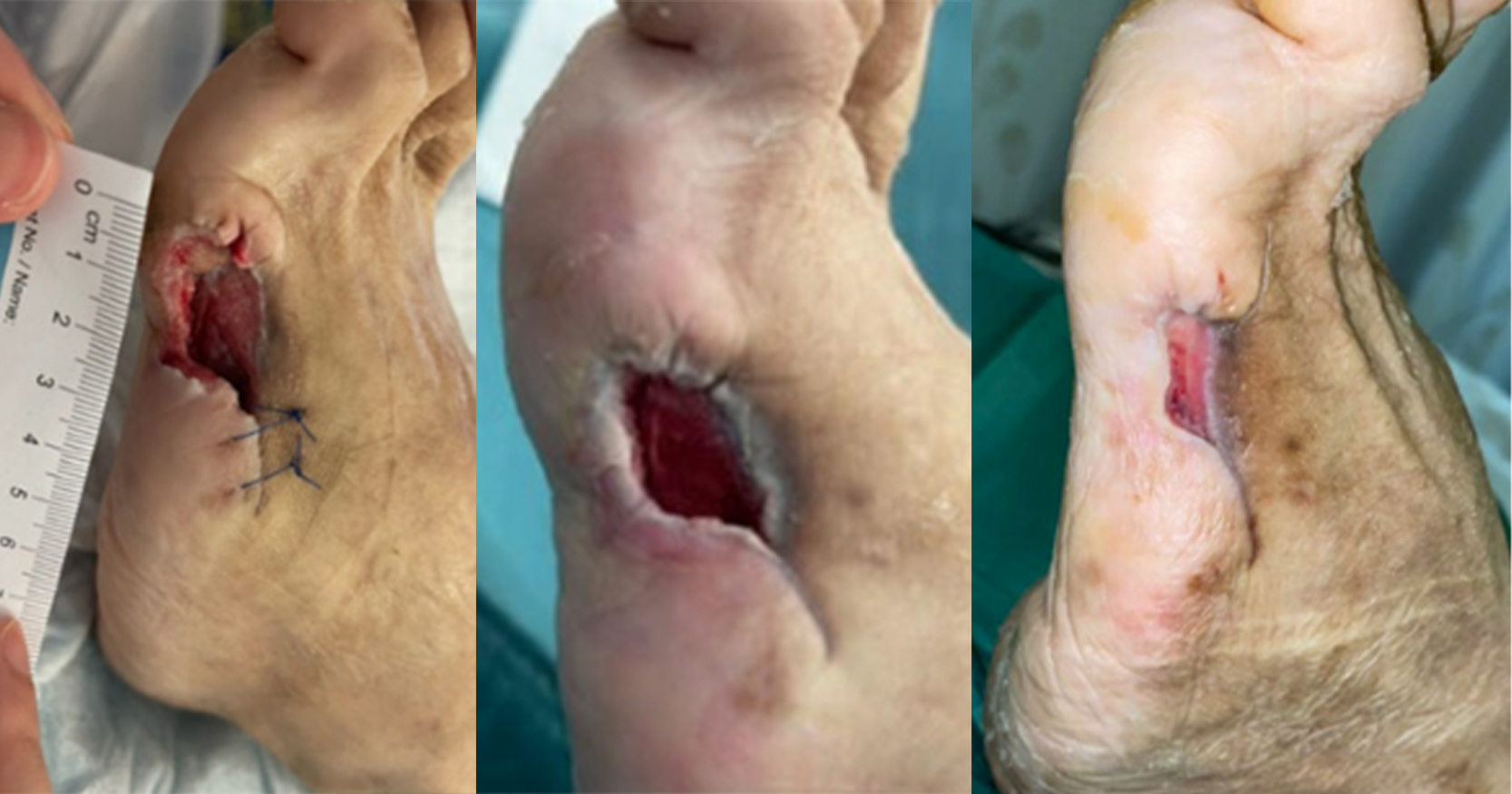
The role of limb salvage is to restore and maintain stability and ambulation. Some surgeons, who are advocates of limb salvage procedures, often delay amputation, leading to worsening of patients’ clinical condition and to multiple operative procedures, eventually resulting in a major limb amputation. Other clinicians do an outright major limb amputation even in mild to moderate diabetic foot syndrome. The goal of this study is to establish predictive factors of the success or failure of a limb saving procedures among patients with diabetic foot ulcers. The result of this study showed that the higher the grade of PEDIS classification increases the probability of the failure of limb salvage procedures Non-significant predictors of failure of limb salvage procedures included age, gender, presence of foot ischaemia, presence of peripheral neuropathy, presence of myocardial infarction and the presence of diabetic nephropathy. Despite the identification of the variables probability to the outcome of limb salvage procedures, the results have limited clinical use. It is recommended that this will be validated with a larger group of patients, to determine if the factors affect the result of limb saving procedures.