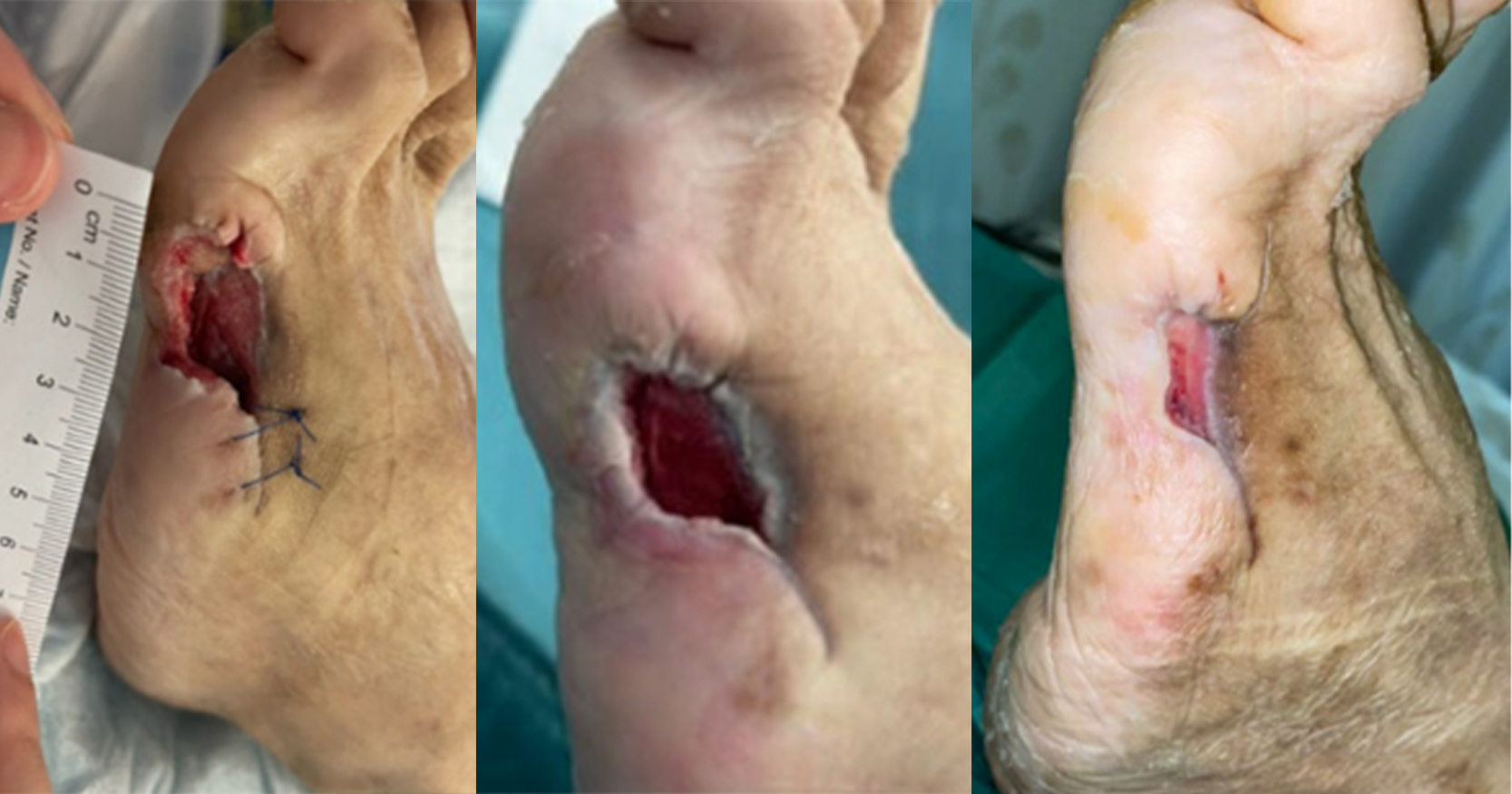
Background: A decrease in blood circulation in diabetic foot ulcers (DFU) leads to a reduction in the angiogenesis process, macrophages function, neutrophils, and growth factors, which in turn slow the healing process. However, electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) can be used to stimulate the muscle that leads to the lower limbs, increasing local blood circulation. Aim: This study was conducted to identify changes in the ABI and the wound development score following EMS in DFUs. Methods: We used sequential sampling of respondents who met the inclusion criteria. The control group received standard wound care, while the intervention group received standard wound care plus EMS therapy. EMS intervention was performed for 4 weeks for 30 minutes per day. Result: The intervention group that received standard wound care plus the EMS had better-wound healing than the group that only received standard wound care. Conclusion: EMS can increase nitric oxide, which causes vasodilation of the blood vessels and stimulates cell synthesis and migration to the wound area.