Advanced wound care has made major strides in addressing both acute and chronic wounds, responding to a dramatic increase in wound incidence worldwide. Chronic wounds impose a considerable human and economic burden, impacting individuals and society alike (Järbrink et al, 2017). With an aging population and earlier onset of chronic conditions, such as diabetes, this burden is on an upward trajectory (Olsson et al, 2019).
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) has been increasingly favoured worldwide as the preferred method of wound care as it is a versatile system designed to optimize wound healing by applying sub-atmospheric pressure and facilitates the modulation of various local and circulating cytokines and growth factors, promoting an anti-inflammatory response (Ravindhran et al, 2023). It is applicable for managing both acute and chronic wounds, ranging from diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers to open fasciotomy wound (Zaver et al, 2023). Negative pressure wound therapy with instillation (NPWTi) represents an innovative advancement in wound management, amalgamating the principles of standard NPWT with the controlled administration of topical irrigation solutions (Kim et al, 2020).
This approach entails the timed delivery of irrigation fluids, such as saline, distilled water or antimicrobial agents, to the wound bed, concurrent with negative pressure application. Meta-analyses consistently demonstrate that negative pressure wound therapy with instillation and dwell time (NPWTi) outperforms both NPWT and conventional dressings in wound care. They reveal higher rates of complete wound closure and fewer complications associated with NPWTi, making it a superior choice for effective wound management (De Pellegrin et al, 2023).
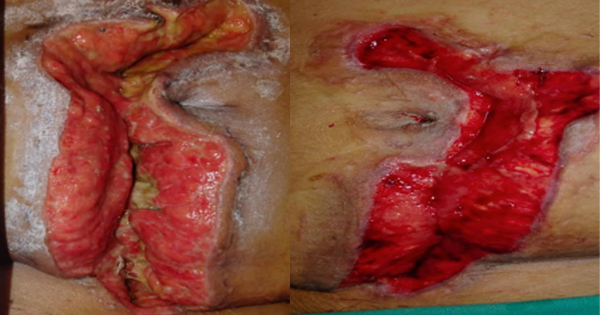
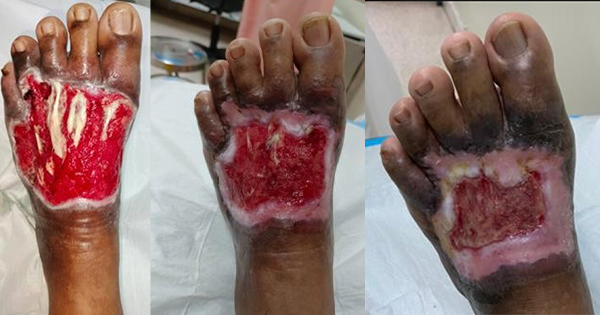
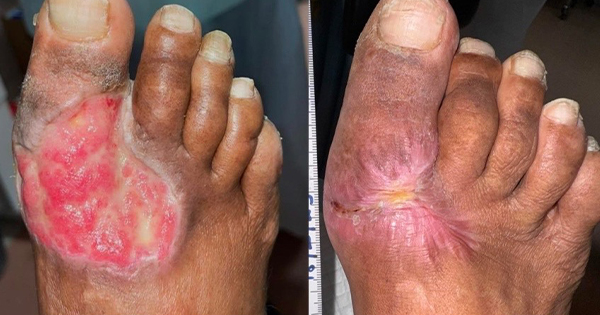
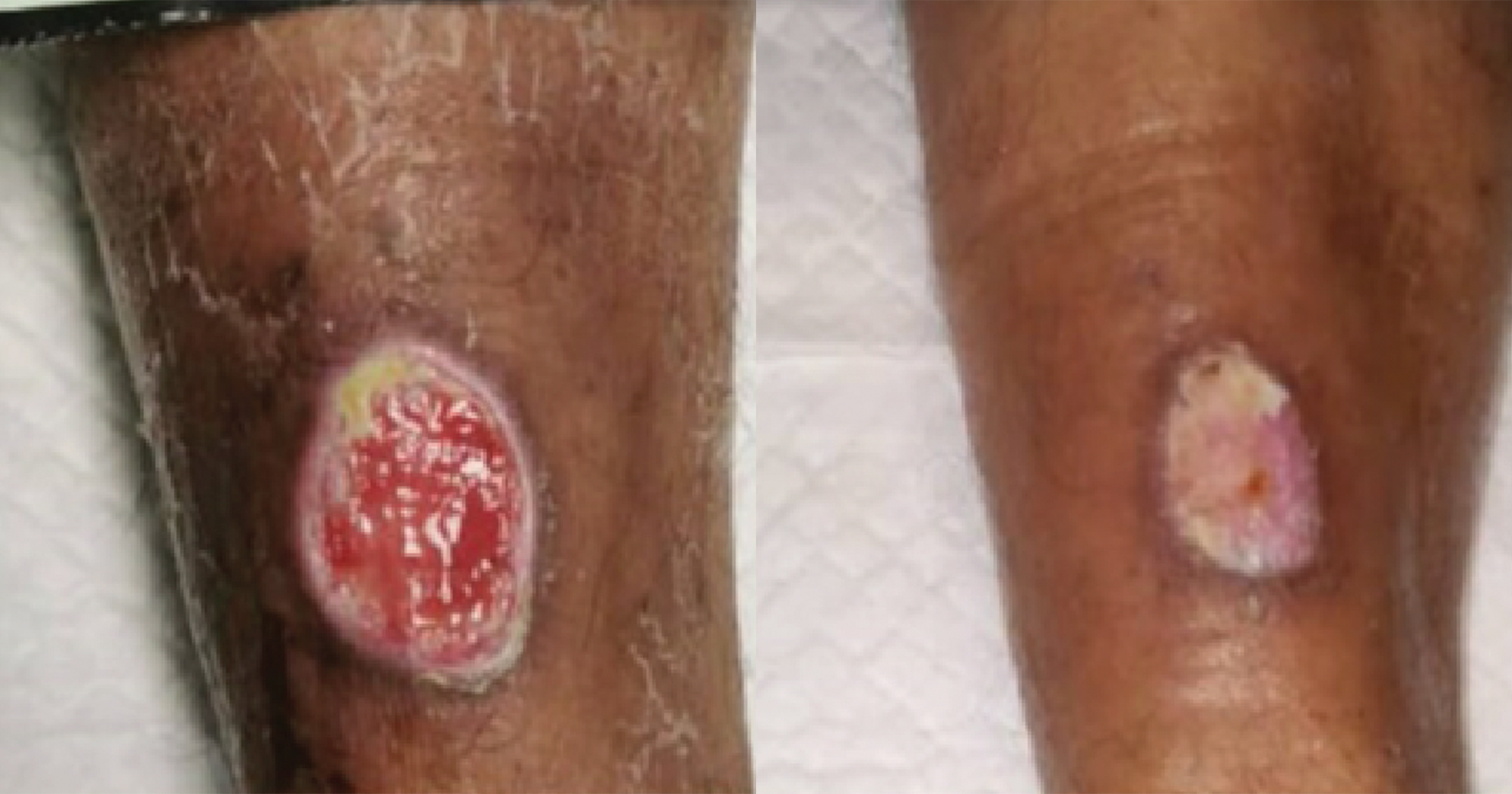
The authors present a case series involving 10 patients with complex wounds stemming from diverse causes. These wounds were treated intermittently with NPWTi using normal saline. The study aimed to underscore the efficacy of NPWTi in addressing a range of difficult wounds.
Materials and methods
The device utilised in this case series was the Genadyne Duo NPWTi, which combines conventional negative pressure with instillation therapy. Patient selection was irrespective of wound type, including wounds unresponsive to standard dressings. Prior to the application of NPWTi, the wound bed was thoroughly cleaned and prepared using aseptic techniques. Ensuring an airtight seal with the adhesive dressing is crucial, as any air leaks can compromise the function and effectiveness of NPWTi. Normal saline was used as the instillation fluid for all wounds, with the volume tailored to the wound area. This volume must be sufficient to cover the wound uniformly without causing leakage or inadequate coverage. It is hypothesised that instillation volume used is one third of the wound volume. The pressure applied and dwell time were adjusted according to the specific wound requirements. In this study, the dressing was changed every 5–7 days.
A total of 10 patients with various types of wounds with no limits to age, gender or types of wounds were selected in this study from Wound Care Department, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Patients and/or their caregivers provided consent for the utilisation of case details and photographs for publication and educational purposes.
Discussion
A total of 10 patients were included in this study ranging from 27 years old to 82 years old with male to female ratio of 1:1. Out of 10 patients, four patients had no comorbidities while two patients have diabetes mellitus and one patient has end-stage renal disease. The treatment cycle and length varies in all patients depending on whether satisfactory wound healing progress has been achieved. In this case series, there were no adverse effect reported in all the patients. The dressing change for each patient in this study ranges from 5 to 7 days considering patient’s comfort and cost of treatment. According to Kim YH et al (2015), 7-day interval changes of NPWTi is comparable to 3-day interval change with cost effectiveness.
The study highlights the efficacy of NPWTi with normal saline in managing both acute and chronic wounds. All patients experienced notable benefits, including the formation of new granulation tissue, absence of infection, and reduced wound size in some cases. The selection of normal saline as the instillation fluid is supported by previous research, such as the work by Kim et al (2015). Additionally, international consensus recommends normal saline as the preferred instilled solution for NPWTi further reinforcing its effectiveness and widespread acceptance in clinical practice (Kim et al, 2013; 2015).
Prior to undergoing NPWTi, all patients had previously tried conventional wound dressings without success. A retrospective study conducted by Gabriel et al (2008) demonstrated that NPWTi significantly reduced the microbial burden of wounds, expedited wound healing, and shortened hospitalisation time when compared to traditional wound treatments for various complex infected wounds.
Moreover, NPWTi has been found to be beneficial in the management of sacral and ischial pressure ulcers. It facilitates wound irrigation, removes fibrinous debris and promotes granulation tissue formation, thereby reducing the need for operative debridement (Arowojolu and Writh, 2021). This highlights the efficacy of NPWTi in addressing challenging wounds and improving patient outcomes.
Limitations
This study has several limitations worth noting. Firstly, its small sample size and the diverse nature of the wounds limit the generalisability of the findings. With a larger sample size, it would be possible to categorise wounds more accurately and consider patients’ comorbidities, which could provide deeper insights into wound healing dynamics.
Secondly, the study did not account for factors such as patients’ nutritional status, control of comorbidities, history of smoking or previous experiences with poor wound healing. These factors can significantly influence wound healing outcomes and could have provided valuable context to the study results. Future research should consider incorporating these variables to better understand their impact on wound healing and treatment efficacy.
Conclusion
The results have shown that the use of NPWTi is efficacious in various types of complex wounds with even just one cycle. Despite the limited sample size, the study highlights the utility of NPWTi-d as a valuable addition to a healthcare provider’s toolkit for managing challenging wounds. It underscores the device’s effectiveness in promoting wound closure, offering clinicians a beneficial option for addressing complex cases.