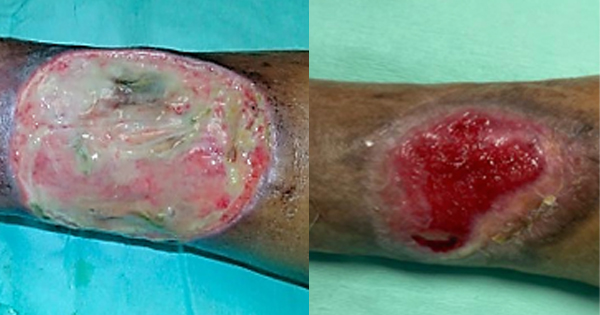
Some wounds persist for months or years (Krasner et al, 2014). Non-healing wounds may be a result of host factors, such as inadequate vasculature, medications that interfere with the healing process, immunocompromised status or critically-ill status with non-modifiable risk factors (terminal disease, end-stage organ failure and other life-threatening health conditions). Among patients who are dying, receiving hospice or palliative care, non-healing or palliative wounds can be associated with complications (Alvarez et al, 2016). An inter-professional approach is required to meet whole-person care needs, especially for those with terminal illness, chronic debilitating diseases, advanced diseases associated with major organ failure (renal, hepatic, pulmonary or cardiac), profound dementia, complex psychosocial issues, diminished self-care abilities and challenging wound-related symptoms (Krasner and Stewart, 2015)