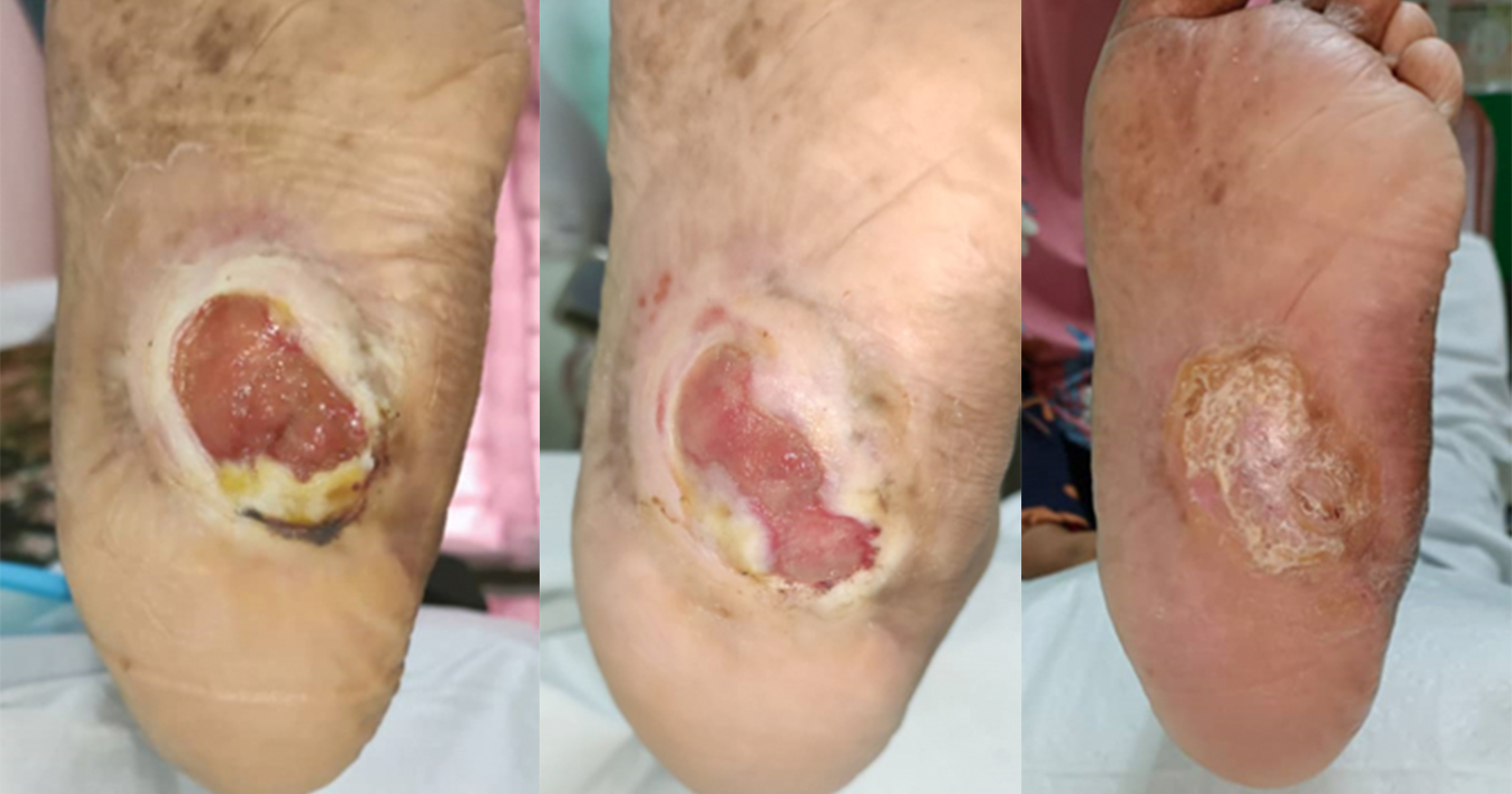
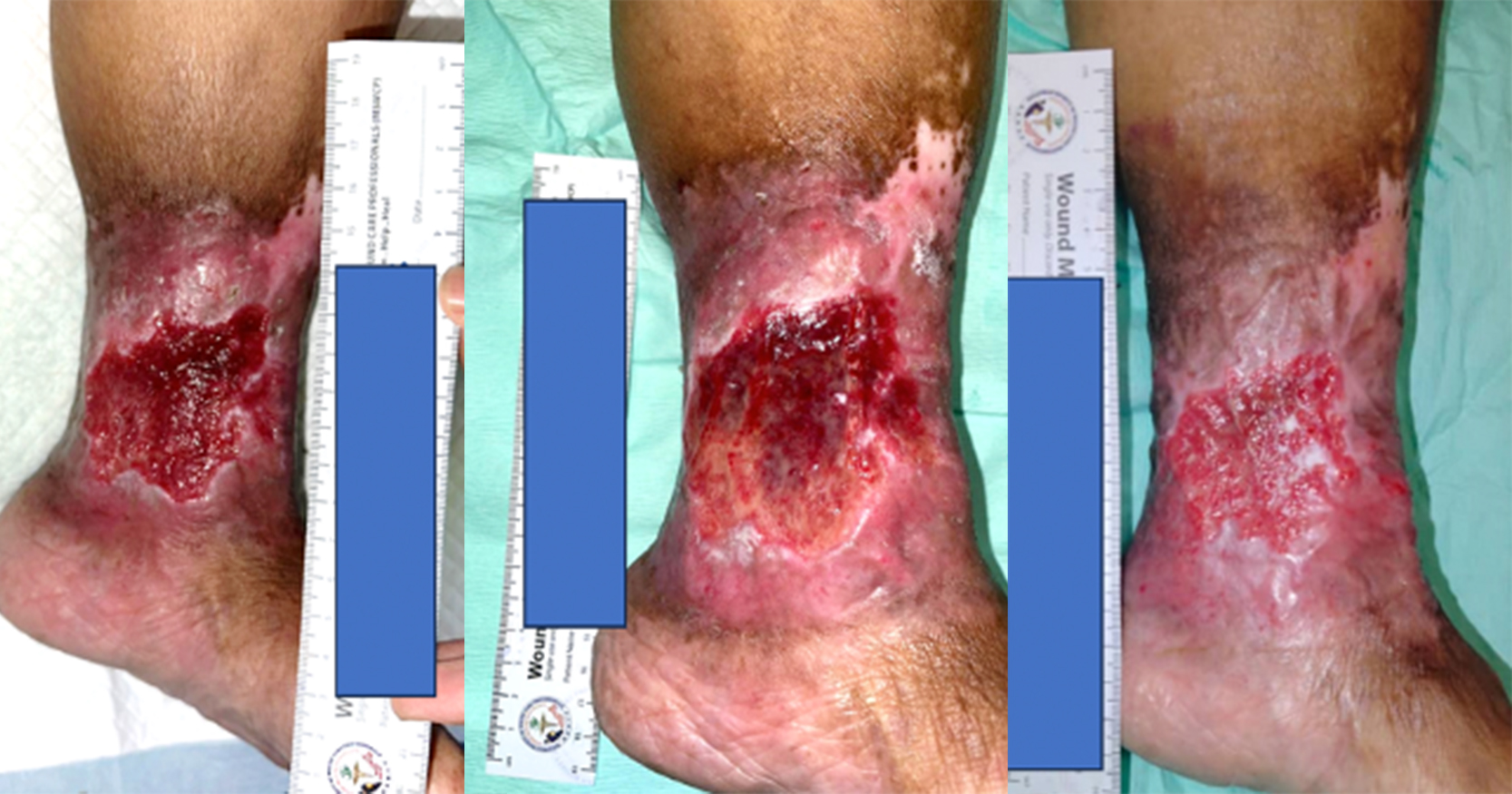
Wound bed preparation is an important concept that encompasses the importance of debridement. The use of proteolytic enzymes is one method of wound debridement. Collagenase is a naturally occurring proteolytic enzymes which is also available as a commercial product which is used for debridement. Collagenase has been shown to be useful for debridement due to its ability to degrade collagen and elastin. This case series reviews eight patients with chronic wounds of different etiologies including diabetes mellitus (n=6), bullous cellulitis (n=1), thigh abscess (n=1). All patients had sloughy, necrotic tissue in the wound bed. Wounds were evaluated using the TIMES concept before cleansed with polyhexamethylene biguanide with betaine (PHMB) solution. Patients were assessed for pain using the Visual Analog Pain Score during each visit. Hyaluronic acid and collagenase (hyaluronic acid sodium salt 0.2% + collagenase) ointment was applied to the wound. Barrier cream was applied to protect the surrounding periwound area. A polyurethane foam dressing was used as the secondary dressing. Patients were followed-up twice a week until the wound was clean and granulating. In this case series, the combined action of hyaluronic acid and collagenase ointment demonstrated a reduction in healing time while improving healing quality although there was limited change seen in relation to pain. There were no adverse events reported. The limitation in this study is that only 8 cases were chosen and this number is a small sample size compared to the population.