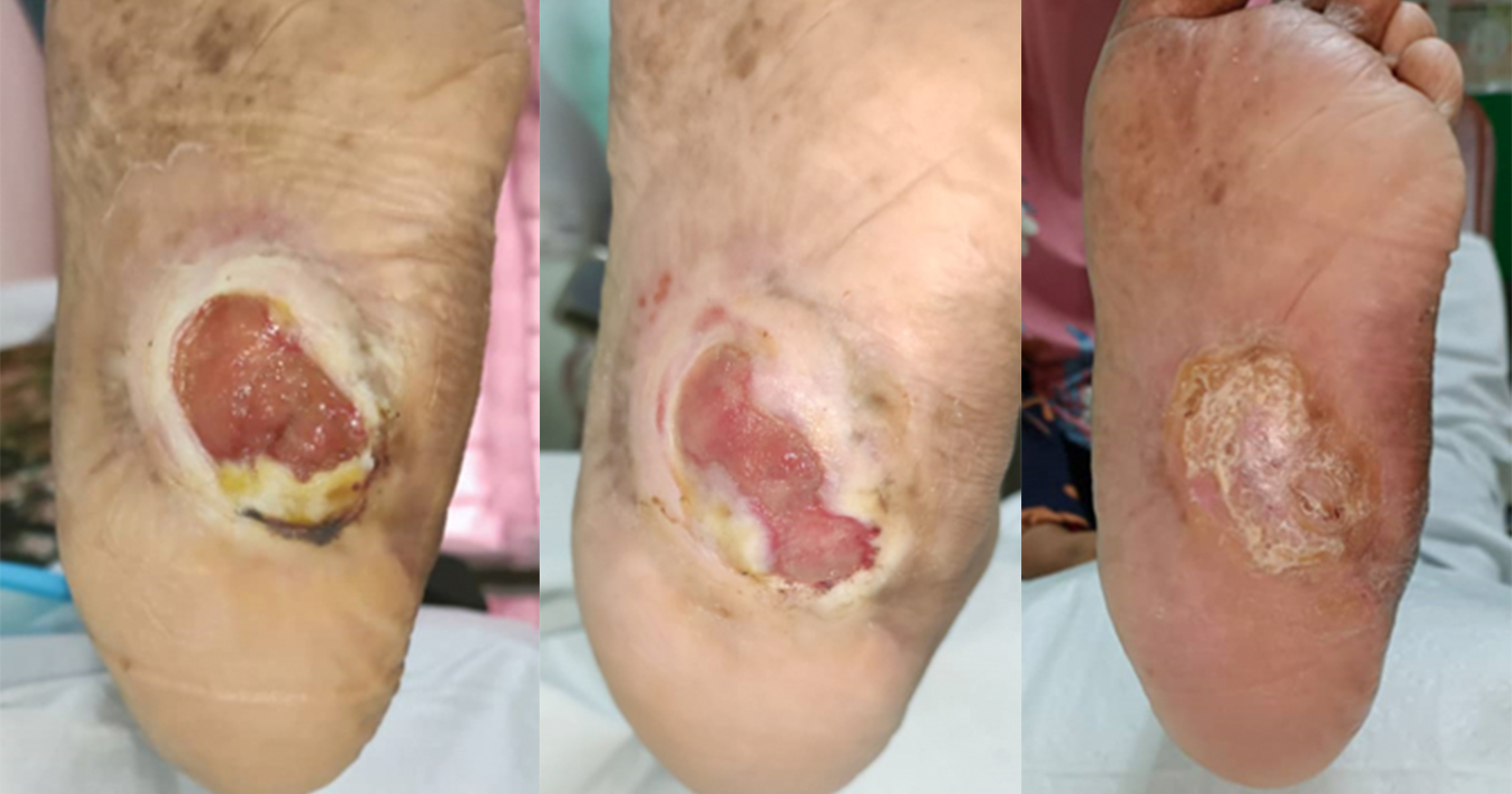
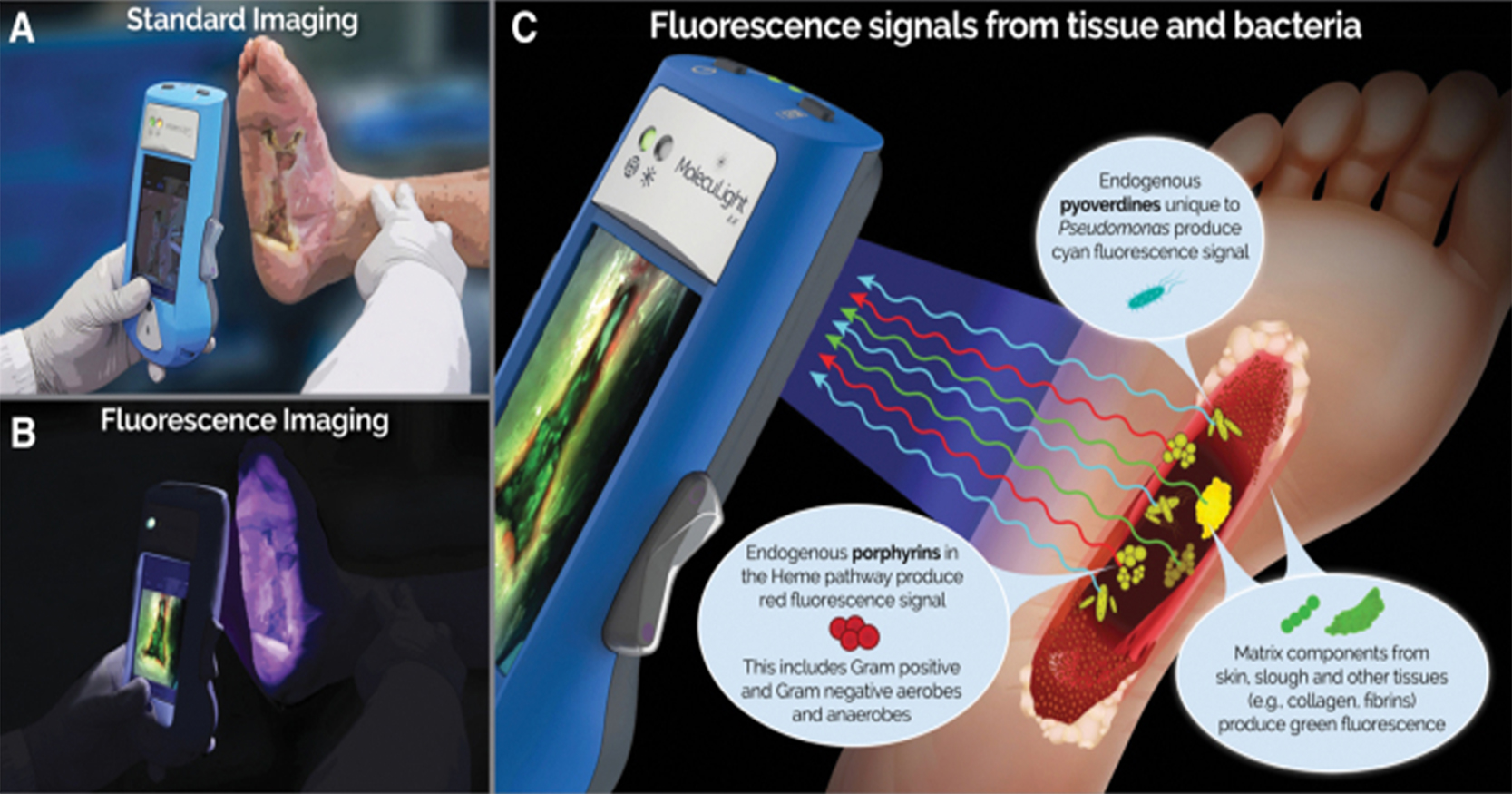
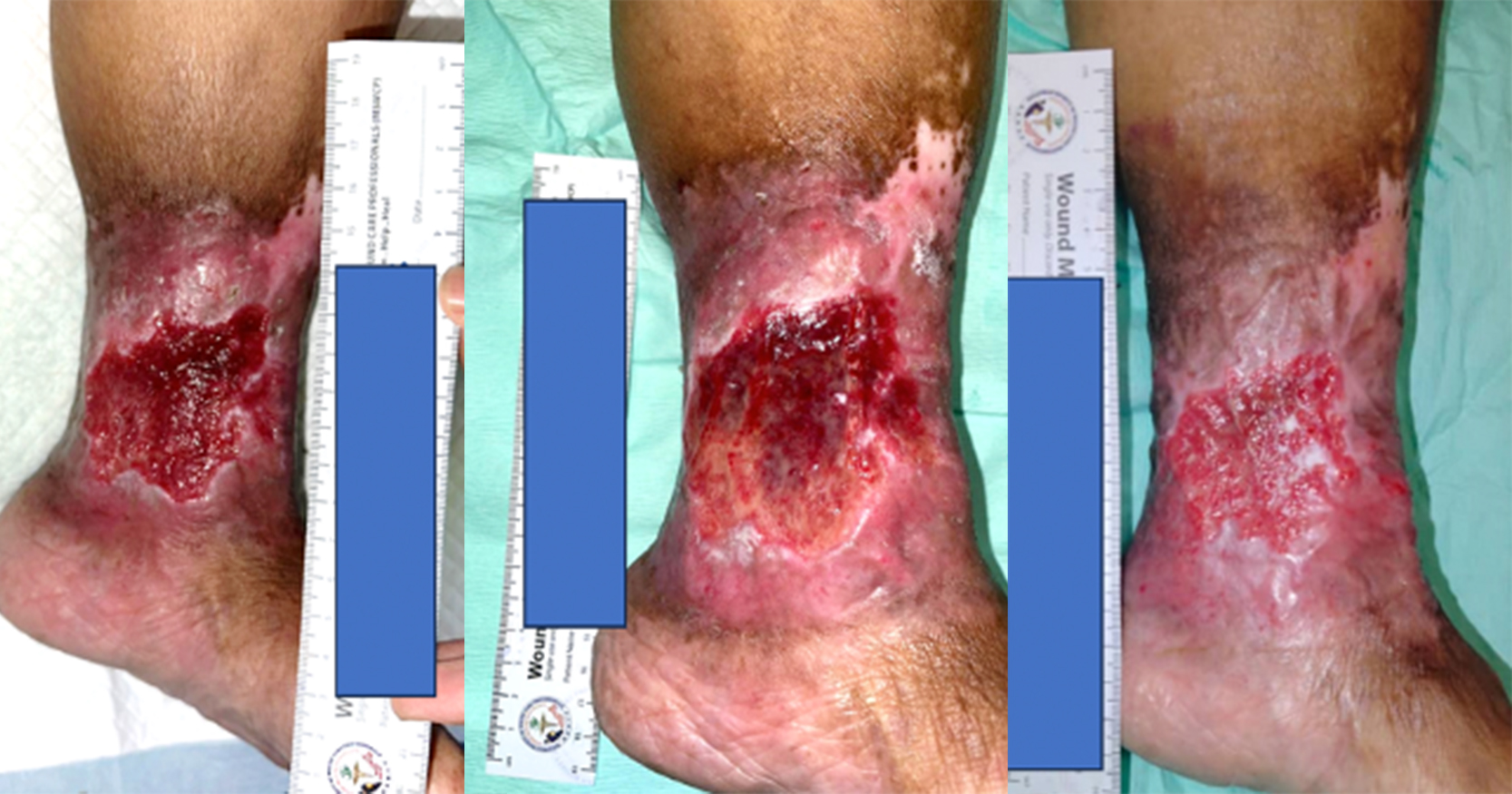
Chronic wounds have been well known to negatively impact on a patients quality of life (QoL). Chronic wounds and illnesses such as diabetes mellitus are chronic inflammatory states and are associated with increased energy expenditure and catabolism of lean body mass. This causes a decline in nutritional status, which in turn prevents wound healing. Studies have demonstrated that incorporating immunonutrition into standard of care can reduce inflammatory biomarkers and increase serum albumin levels in critically ill patients. This study aims to demonstrate the effect of supplementing standard wound care with immunonutrition (NeoMune enteral formula, Thai Otsuka Pharmaceuticals Co. Ltd, Thailand) on the serum albumin and wound healing of patients with chronic wounds. This study had shown a modest increase in our patients’ serum albumin levels over the 14 days of consuming the protein-based supplement. A majority of them also showed reduction in wound size in addition to a healthier looking wound base.