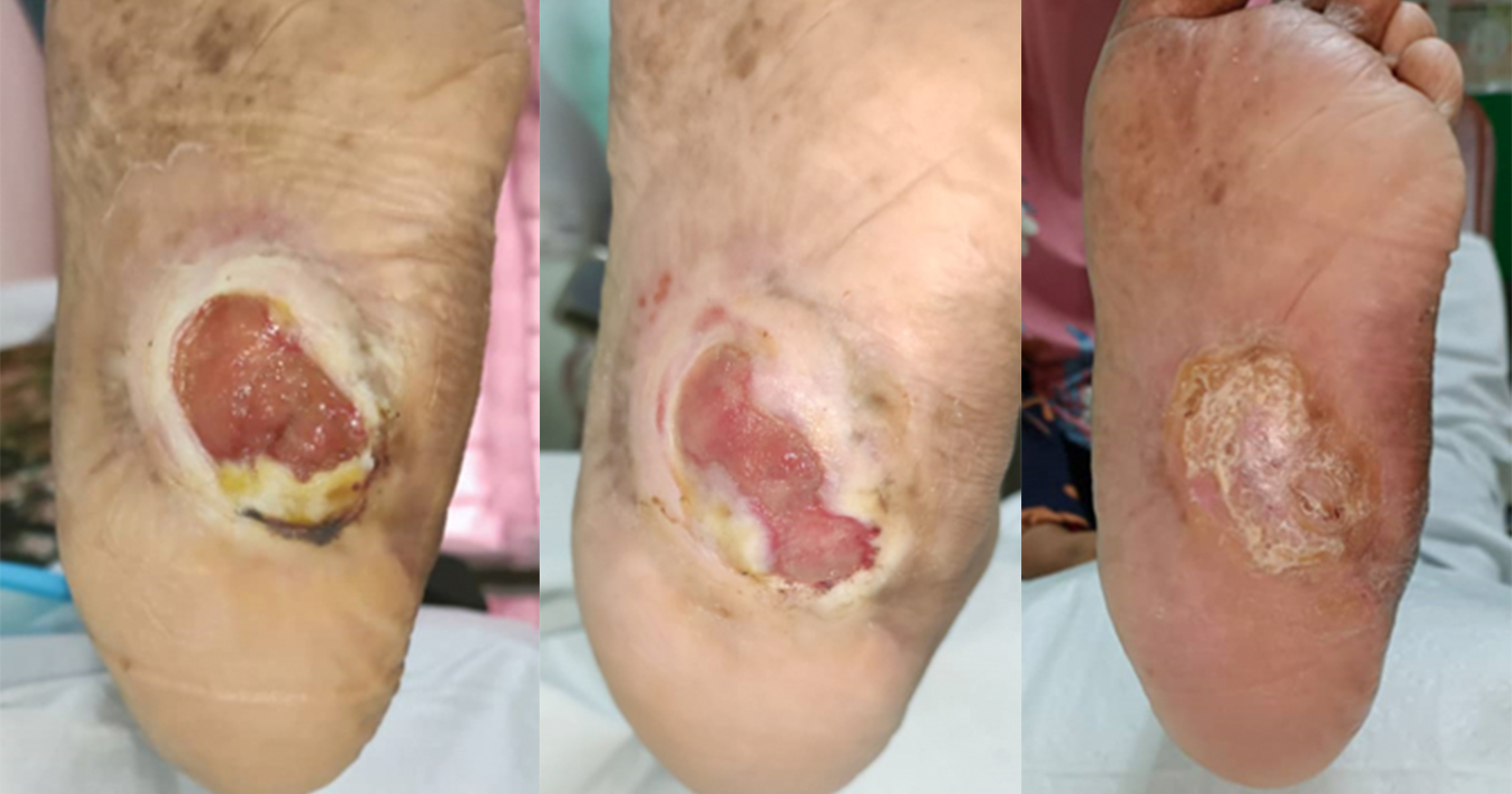
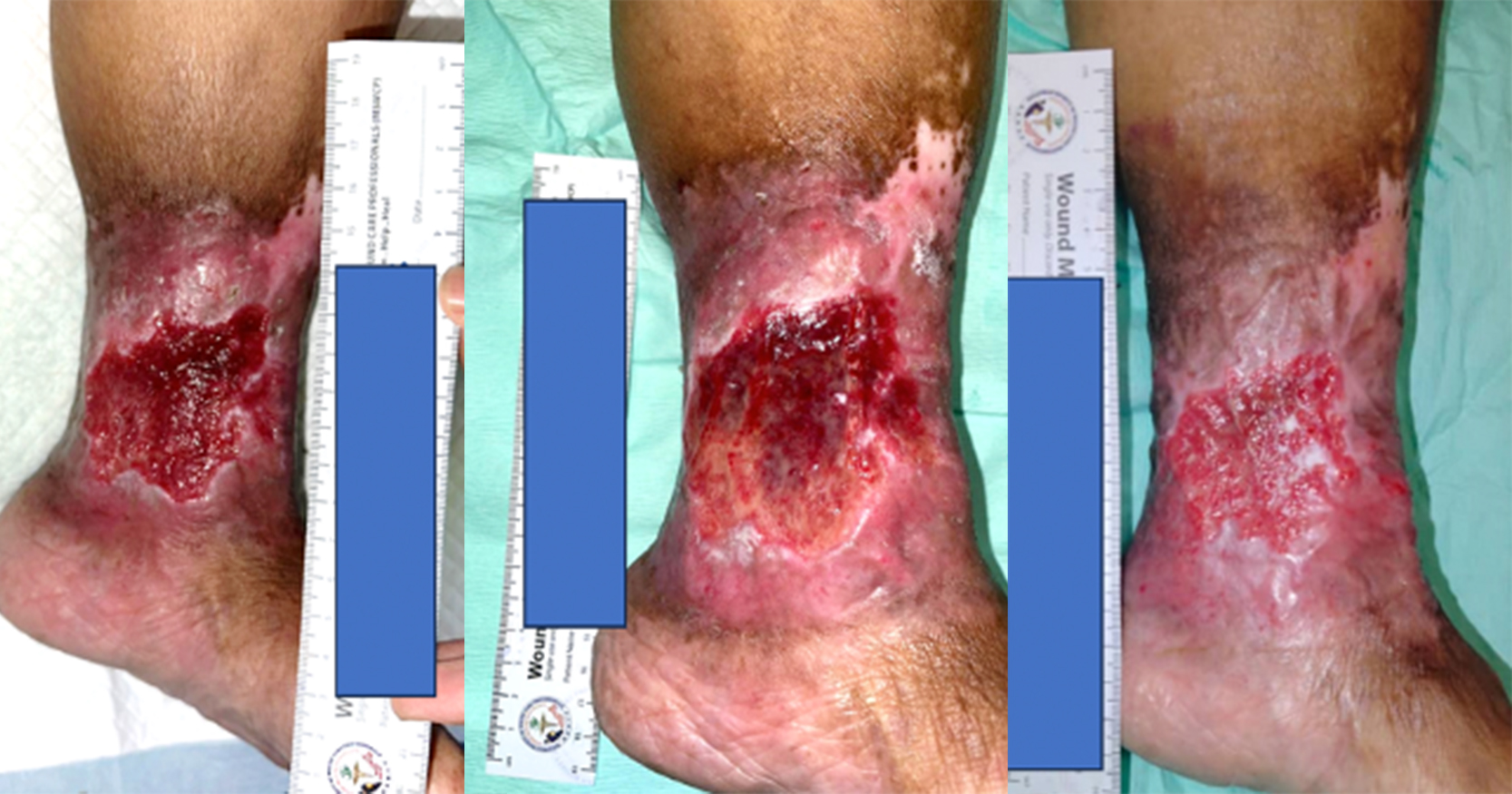
Advanced wound dressings have evolved to do more than just providing moist wound environment for better wound healing. Here we measure the wound healing efficacy of a new hydrogel as shown by the reduction in wound area reduction. This case series includes ten patients with chronic wounds of different aetiologies, diabetes foot ulcers (DFU), infected wounds, postsurgical wounds and pressure ulcers (PU). We included patients with sloughy or necrotic wounds in this study. Wounds were first evaluated by using the TIME concept before cleansing with sterile water. Patients were assessed for pain using the Visual Pain Score of 1 to 10 on each visit. Anscare Healus Wound Gel was applied to the wound as per standard of care (twice a week) and polyurethane foam was used as the secondary dressing. Patient follow-up was twice a week until wound was healed. There was noteworthy improvement in all ten cases in terms of reduction in wound size. The percentage of wound reduction ranges from 83.8% to 100%. There is little to no change in the pain score experience by patients, as most of the patients has diabetes mellitus, this was probably due to diabetic neuropathy. Anscare Healus Wound Gel used in this study, provides a moisture-balanced environment for wound healing while promoting autolytic debridement by using the body’s production of enzymes and moisture. The wound gel can soften eschar and replace necrotic tissue, promoting autolytic debridement with superior exudates absorption. The Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium in the gel, has antimicrobial action, antibiofilm action and promotes wound healing by restoring the normal structural and functional characteristics of the skin. Alginate dressings absorb fluid from the wound and help to maintain a physiologically moist environment that minimises bacterial infections at the wound site. The wound gel provides a moisture-balanced environment for the wound bed, keeping the wound bed moist for better wound healing and pain-free experience.